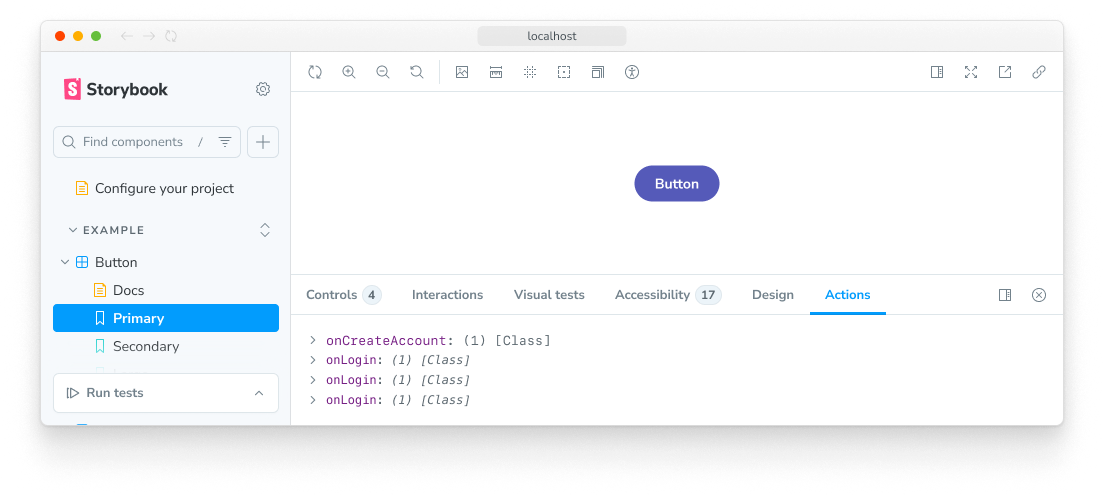
Actions
操作用于显示事件处理程序(回调)已被调用,以及显示其参数。操作面板可以显示故事参数和其他函数调用。
故事参数
操作通过提供 Storybook 生成的特殊模拟函数来工作,以用于故事的事件处理程序参数。有两种方法可以获取操作参数:
通过 storybook/test fn 模拟
编写操作的推荐方式是使用 `storybook/test` 中的 `fn` 工具来模拟和监视参数。这对于编写交互测试非常有用。您可以通过将组件的方法赋值给 `fn()` 函数来模拟它们。
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, vue3-vite, etc.
import type { Meta } from '@storybook/your-framework';
import { fn } from 'storybook/test';
import { Button } from './Button';
const meta = {
component: Button,
// 👇 Use `fn` to spy on the onClick arg, which will appear in the actions panel once invoked
args: { onClick: fn() },
} satisfies Meta<typeof Button>;
export default meta;如果您的组件调用了参数(由于用户交互或 `play` 函数),并且该参数已被监视,则该事件将显示在操作面板中。
自动匹配参数
另一种选择是使用全局参数来匹配与特定模式匹配的所有 argTypes。以下配置会自动为每个 `on` argType 创建操作(您可以手动指定,或者可以自动推断)。
这在组件有数十(或数百)个方法且您不想为每个方法手动应用 `fn` 工具时非常有用。但是,**这不是推荐** 的编写操作方式。因为自动推断的参数**在 play 函数中不可用作监视器**。如果您使用 `argTypesRegex` 并且您的故事有 play 函数,您还需要使用 `fn` 工具定义参数才能在 play 函数中对其进行测试。
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, vue3-vite, etc.
import type { Preview } from '@storybook/your-framework';
const preview: Preview = {
parameters: {
actions: { argTypesRegex: '^on.*' },
},
};
export default preview;如果您需要更精细地控制匹配哪些 `argTypes`,您可以调整您的故事并包含 `argTypesRegex` 参数。例如:
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, vue3-vite, etc.
import type { Meta } from '@storybook/your-framework';
import { Button } from './Button';
const meta = {
component: Button,
parameters: { actions: { argTypesRegex: '^on.*' } },
} satisfies Meta<typeof Button>;
export default meta;这将把一个标准的 HTML 事件处理程序绑定到您的组件渲染的最外层 HTML 元素,并在事件被调用(针对给定选择器)时触发一个操作。格式为 `
非故事函数调用
如果需要记录与任何故事无关的函数调用,仍然可以使用操作面板。这对于调试或日志记录很有帮助。主要有两种方法可以做到这一点:`storybook/test` 中的 `spyOn` 或 `storybook/actions` 中的 `action` 函数。对于基本日志记录,我们建议创建一个函数监视器,对于更复杂的场景,您可以直接使用 `action` 函数。
通过 storybook/test spyOn
`storybook/test` 中的模拟和监视器会自动记录为操作。在操作面板中显示函数调用的最简单方法是使用 `spyOn` 工具函数。监视器会显示一个默认名称,您可以通过调用 `mockName` 方法来自定义此名称。
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using (e.g., react-vite, nextjs, svelte)
import type { Preview } from '@storybook/your-framework';
import { spyOn } from 'storybook/test';
const preview: Preview = {
async beforeEach() {
spyOn(console, 'log').mockName('console.log');
},
};
export default preview;通过 `action` 函数
为了过滤哪些函数调用被记录,您可以覆盖 `spyOn` 函数的行为,提供一个自定义实现,只有在满足特定条件时才调用 `storybook/actions` 中的 `action` 函数,以防止它记录所有对被监视函数的调用。
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using (e.g., react-vite, nextjs, svelte)
import type { Preview } from '@storybook/your-framework';
import { action } from 'storybook/actions';
import { spyOn } from 'storybook/test';
const originalConsoleLog = console.log;
const preview: Preview = {
async beforeEach() {
spyOn(console, 'log')
// Disable automatic logging in the actions panel
.mockName('')
.mockImplementation((args) => {
// Check if the log message matches a certain pattern
if (someCondition(args)) {
// Manually log an action
action('console.log')(args);
}
// Call the original console.log function
originalConsoleLog(...args);
});
},
};
export default preview;API
参数
这会将以下 参数 贡献给 Storybook,位于 `actions` 命名空间下。
argTypesRegex
类型:string
为匹配正则表达式的每个参数创建操作。请注意此方法的重大限制,如上所述。
disable
类型:boolean
禁用操作面板。
此参数对于允许在更具体的级别进行覆盖非常有用。例如,如果此参数在项目级别设置为 `true`,则可以通过在 meta(组件)或 story 级别将其设置为 `false` 来重新启用它。
导出
import { action } from 'storybook/actions';action
类型:(name?: string) => void
允许您创建一个操作,当在 Storybook UI 中点击时,它会显示在操作面板中。操作函数接受一个可选的名称参数,该参数用于在 UI 中标识该操作。
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, vue3-vite, etc.
import type { Meta } from '@storybook/your-framework';
import { action } from 'storybook/actions';
import Button from './Button';
const meta = {
component: Button,
args: {
// 👇 Create an action that appears when the onClick event is fired
onClick: action('on-click'),
},
} satisfies Meta<typeof Button>;
export default meta;