Jest 中的可移植故事
如果您正在使用 实验性的 CSF Factories 格式,则无需使用可移植故事 API。相反,您可以 直接导入和使用您的故事。
可移植故事是 Storybook 故事,可以在外部环境中使用,例如 Jest。
通常,Storybook 会自动组合故事及其 注解,作为 故事流程 的一部分。当在 Jest 测试中使用故事时,您必须自己处理故事流程,这就是 composeStories 和 composeStory 函数实现的功能。
此处指定的 API 在 Storybook 8.2.7 及更高版本中可用。如果您使用的是旧版本的 Storybook,可以升级到最新版本(npx storybook@latest upgrade)来使用此 API。如果您无法升级,可以使用之前的 API,它使用 .play() 方法而不是 .run(),但其他方面是相同的。
正在使用 Next.js? 在 Jest 中使用 Next.js 项目的可移植故事时,您需要做三项不同的事情
- 配置
next/jest.js转换器,它将为您处理所有必要的 Next.js 配置。 - 从
@storybook/nextjs包导入composeStories或composeStory(例如import { composeStories } from '@storybook/nextjs')。 - 设置 内部模块别名 以确保框架配置正常工作并能够对其进行模拟和断言。
composeStories
composeStories 将处理您指定的组件的故事,将每个故事与必要的 注解 组合,并返回一个包含组合后故事的对象。
默认情况下,组合后的故事将使用故事中定义的 args 渲染组件。您也可以将任何 props 传递给测试中的组件,这些 props 将覆盖故事 args 中传递的值。
import { test, expect } from '@jest/globals';
import { render, screen } from '@testing-library/react';
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, nextjs-vite, etc.
import { composeStories } from '@storybook/your-framework';
// Import all stories and the component annotations from the stories file
import * as stories from './Button.stories';
// Every component that is returned maps 1:1 with the stories,
// but they already contain all annotations from story, meta, and project levels
const { Primary, Secondary } = composeStories(stories);
test('renders primary button with default args', () => {
render(<Primary />);
const buttonElement = screen.getByText('Text coming from args in stories file!');
expect(buttonElement).not.toBeNull();
});
test('renders primary button with overridden props', () => {
// You can override props and they will get merged with values from the story's args
render(<Primary>Hello world</Primary>);
const buttonElement = screen.getByText(/Hello world/i);
expect(buttonElement).not.toBeNull();
});Type
(
csfExports: CSF file exports,
projectAnnotations?: ProjectAnnotations
) => Record<string, ComposedStoryFn>参数
csfExports
(必需)
类型: CSF 文件导出
指定您想组合哪个组件的故事。传递 CSF 文件的 **完整导出集**(而不是默认导出!)。例如:import * as stories from './Button.stories'
projectAnnotations
Type: ProjectAnnotation | ProjectAnnotation[]
指定要应用于组合后故事的项目注解。
此参数是为方便起见提供的。您可能应该使用 setProjectAnnotations 而不是它。关于 ProjectAnnotation 类型的详细信息可以在该函数的 projectAnnotations 参数中找到。
此参数可用于 覆盖 通过 setProjectAnnotations 应用的项目注解。
Return
类型:Record<string, ComposedStoryFn>
一个对象,其中键是故事的名称,值是组合后的故事。
此外,组合后的故事将具有以下属性
| Property | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| args | Record<string, any> | 故事的 args |
| argTypes | ArgType | 故事的 argTypes |
| id | string | 故事的 id |
| parameters | Record<string, any> | 故事的 parameters |
| play | (context) => Promise<void> | undefined | 执行给定故事的 play 函数 |
| run | (context) => Promise<void> | undefined | 挂载并执行给定故事的 play 函数 |
| storyName | string | 故事的名称 |
| tags | string[] | 故事的 tags |
composeStory
如果您想为一个组件组合单个故事,可以使用 composeStory。
import { jest, test, expect } from '@jest/globals';
import { render, screen } from '@testing-library/react';
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, nextjs-vite, etc.
import { composeStory } from '@storybook/your-framework';
import meta, { Primary as PrimaryStory } from './Button.stories';
test('onclick handler is called', () => {
// Returns a story which already contains all annotations from story, meta and global levels
const Primary = composeStory(PrimaryStory, meta);
const onClickSpy = jest.fn();
await Primary.run({ args: { ...Primary.args, onClick: onClickSpy } });
const buttonElement = screen.getByRole('button');
buttonElement.click();
expect(onClickSpy).toHaveBeenCalled();
});Type
(
story: Story export,
componentAnnotations: Meta,
projectAnnotations?: ProjectAnnotations,
exportsName?: string
) => ComposedStoryFn参数
story
(必需)
类型:Story export
指定您想组合的故事。
componentAnnotations
(必需)
类型:Meta
故事文件中包含 story 的默认导出。
projectAnnotations
Type: ProjectAnnotation | ProjectAnnotation[]
指定要应用于组合后故事的项目注解。
此参数是为方便起见提供的。您可能应该使用 setProjectAnnotations 而不是它。关于 ProjectAnnotation 类型的详细信息可以在该函数的 projectAnnotations 参数中找到。
此参数可用于 覆盖 通过 setProjectAnnotations 应用的项目注解。
exportsName
类型:string
您可能不需要这个。因为 composeStory 接受单个故事,它无法访问该故事在文件中的导出名称(就像 composeStories 那样)。如果您必须确保测试中的故事名称唯一且不能使用 composeStories,您可以在此处传递故事导出的名称。
Return
类型:ComposedStoryFn
单个 组合后故事。
setProjectAnnotations
此 API 应在测试运行之前,通常在 setup 文件 中调用一次。这将确保每当调用 composeStories 或 composeStory 时,都会同时考虑项目注解。
这些是 setup 文件中需要的配置
- preview 注解:在
.storybook/preview.ts中定义的注解 - addon 注解(可选):由 addons 导出的注解
- beforeAll:在所有测试之前运行的代码(更多信息)
import { beforeAll } from '@jest/globals';
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, nextjs-vite, etc.
import { setProjectAnnotations } from '@storybook/your-framework';
// 👇 Import the exported annotations, if any, from the addons you're using; otherwise remove this
import * as addonAnnotations from 'my-addon/preview';
import * as previewAnnotations from './.storybook/preview';
const annotations = setProjectAnnotations([previewAnnotations, addonAnnotations]);
// Supports beforeAll hook from Storybook
beforeAll(annotations.beforeAll);有时故事可能需要插件的 decorator 或 loader 才能正确渲染。例如,插件可以应用一个 decorator,该 decorator 将您的故事包装在必要的路由上下文中。在这种情况下,您必须在项目注解中包含该插件的 preview 导出。请参阅上面示例中的 addonAnnotations。
注意:如果插件不自动应用 decorator 或 loader 本身,而是将其导出供您在 .storybook/preview.js|ts 中手动应用(例如,使用来自 @storybook/addon-themes 的 withThemeFromJSXProvider),那么您无需执行任何其他操作。它们已包含在上面示例的 previewAnnotations 中。
如果您需要配置 Testing Library 的 render 或使用不同的渲染函数,请在 此讨论 中告诉我们,以便我们了解您的需求。
Type
(projectAnnotations: ProjectAnnotation | ProjectAnnotation[]) => ProjectAnnotation参数
projectAnnotations
(必需)
Type: ProjectAnnotation | ProjectAnnotation[]
一组项目 注解(在 .storybook/preview.js|ts 中定义的)或一组项目注解的数组,它们将应用于所有组合后的故事。
Annotations
注解是应用于故事的元数据,例如 args、decorators、loaders 和 play functions。它们可以为特定故事、组件的所有故事或项目中的所有故事定义。
Story pipeline
要在 Storybook 中预览您的故事,Storybook 会运行一个故事流程,包括应用项目注解、加载数据、渲染故事以及执行交互。这是该流程的简化版本
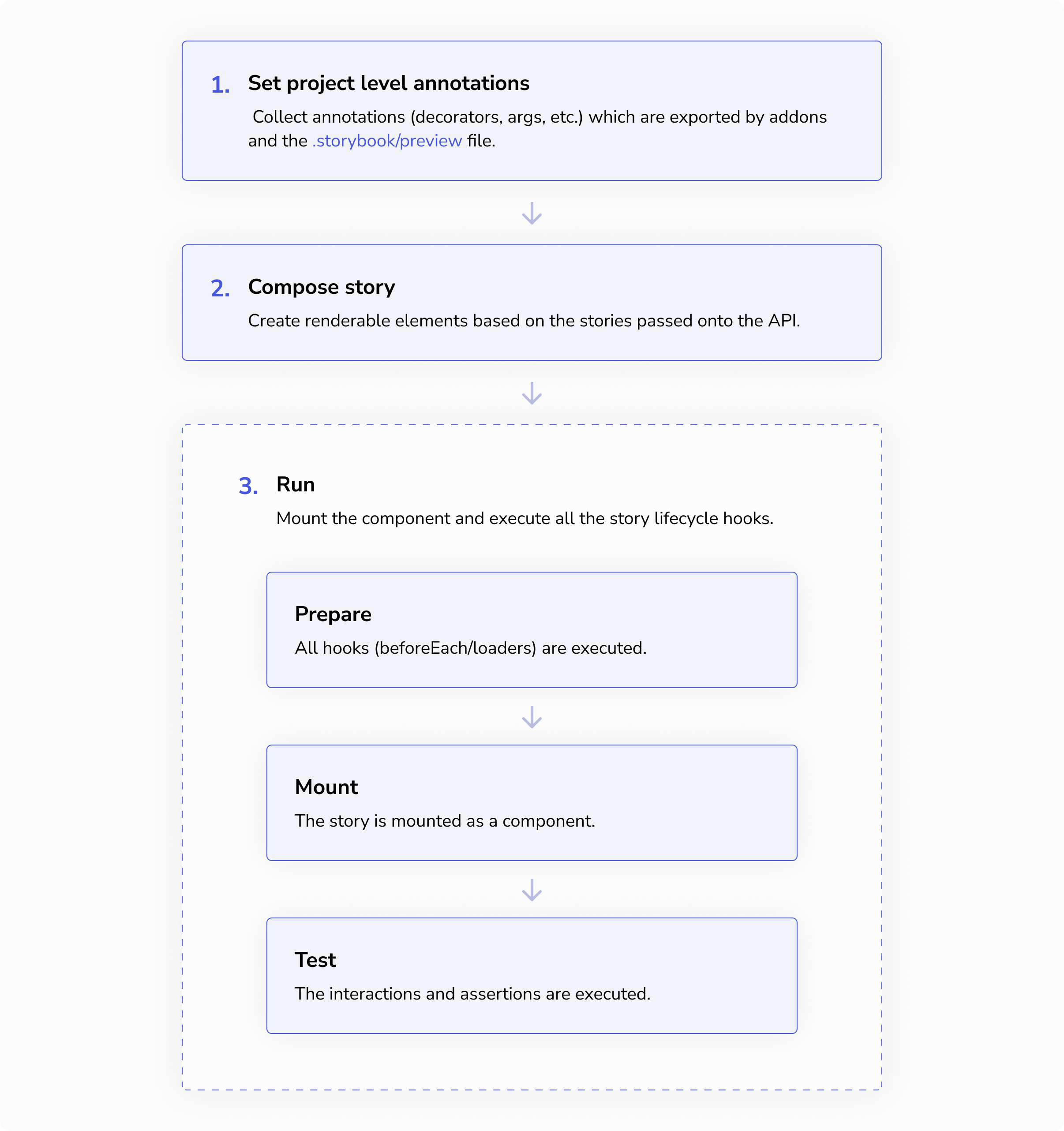
但是,当您想在不同的环境中重用故事时,重要的是要理解所有这些步骤构成了一个故事。可移植故事 API 为您提供了在外部环境中重现该故事流程的机制。
1. 应用项目级注解
Annotations come from the story itself, that story's component, and the project. The project-level annotations are those defined in your .storybook/preview.js file and by addons you're using. In portable stories, these annotations are not applied automatically — you must apply them yourself.
👉 For this, you use the setProjectAnnotations API.
2. 组合
故事通过运行 composeStories 或 composeStory 进行准备。结果是一个可渲染的组件,代表故事的渲染函数。
3. 运行
最后,故事可以通过定义 loaders、beforeEach 或在 mount 时将所有故事代码放在 play 函数中,来准备它们所需的数据(例如,设置一些模拟或获取数据),然后再进行渲染。在可移植故事中,当您调用组合后故事的 run 方法时,所有这些步骤都将执行。
👉 为此,您可以使用 composeStories 或 composeStory API。组合后故事将返回一个要调用的 run 方法。
import { test } from '@jest/globals';
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, nextjs-vite, etc.
import { composeStories } from '@storybook/your-framework';
import * as stories from './Button.stories';
const { Primary } = composeStories(stories);
test('renders and executes the play function', async () => {
// Mount story and run interactions
await Primary.run();
});如果您的 play 函数包含断言(例如 expect 调用),您的测试将在这些断言失败时失败。
Overriding globals
如果您的故事行为因 globals(例如,将文本渲染为英语或西班牙语)而异,您可以通过在组合故事时覆盖项目注解来在可移植故事中定义这些全局值。
import { test } from '@jest/globals';
// Replace your-framework with the framework you are using, e.g. react-vite, nextjs, nextjs-vite, etc.
import { composeStory } from '@storybook/your-framework';
import meta, { Primary as PrimaryStory } from './Button.stories';
test('renders in English', async () => {
const Primary = composeStory(
PrimaryStory,
meta,
{ globals: { locale: 'en' } }, // 👈 Project annotations to override the locale
);
await Primary.run();
});
test('renders in Spanish', async () => {
const Primary = composeStory(PrimaryStory, meta, { globals: { locale: 'es' } });
await Primary.run();
});